Software & Digital Resources
The software and other digital resources below were created as part of the research undertaken at the IoSR.
Contents
Software
MUSHRA test GUI
Get it on GitHub
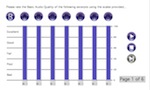
This Max/MSP patcher is designed for conducting MUSHRA (MUltiple Stimulus with Hidden Reference and Anchor, see ITU-R BS.1534) listening tests. The patcher allows the comparison of a number of stimuli (7 by default, although up to 10 is supported) and facilitates repeats. By default, the patcher can compare seven processes applied to three music tracks, with two repeats, making a total of six pages. However, the software can be easily adapted to accommodate a different number of stimuli and/or music tracks and/or repeats; the included documentation describes the procedure in detail.
Requirements: Max/MSP 6 or higher.
[Top]
ABX test GUI
Get it on GitHub
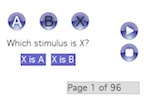
This Max/MSP patcher implements an ABX listening test. The test is a discrimination task, assessing the listener's ability to hear differences in audio files that contain small impairments. The patcher chooses a reference stimulus and a test stimulus, which are randomly assigned to A and B. Either A or B is then randomly assigned to X. This listener must decide whether X is A or B. The patcher chooses the test stimulus from a pool of several audio files. The presentation of each audio file can be repeated a specified number of times. The presentation of all audio files and repeats is randomised.
Requirements: Max/MSP 6 or higher.
[Top]
A localisation- and precedence-based binaural separation algorithm
[Download]
The separation software developed during
Chris Hummersone's PhD is available below. It is based upon Palomäki et al.'s (2004) binaural processor for missing data speech recognition in the presence of noise and small-room reverberation. The software generates "cocktail party" mixtures of signals arising from two spatially-separate sound sources in real rooms and attempts to separate them using interaural cues enhanced by models of the precedence effect. Implemented precedence models include those proposed by Martin (1997), Faller & Merimaa (2004), Lindemann (1986) and Macpherson (1991).
Requirements: MATLAB, Signal Processing Toolbox, compatible C compiler (for Mex functions).
[Top]
Perceptually motivated measurement of spatial sound attributes
[View Project Page]
This software will analyse a binaurally-recorded .wav file, and display predictions of the perceived angular width and direction of the sound as they vary over time.
Requirements: MATLAB, Signal Processing Toolbox.
[Top]
MATLAB toolbox
The IoSR MATLAB Toolbox contains a number of functions and classes for: auditory modelling, signal processing, sound source separation, statistics, plotting, etc.
[Top]
Other Digital Resources
Binaural Room Impulse Responses Captured in Real Rooms
Get it on GitHub
The binaural room impulse responses (BRIRs) used in
A localisation- and precedence-based binaural separation algorithm are packaged with it, but are available separately and at a higher sampling frequency here. The responses were captured in real rooms at the University, with sound sources placed on the frontal azimuthal plane (±90°) in 5° increments. The package includes documentation on how and where the responses were captured. The BRIRs are included as stereo wave files and
spatially-oriented format for acoustics (SOFA) files. They were captured at 48 kHz, 16 bit, but are also included downsampled to 16 kHz.
Requirements: None.
[Top]
Simulated Room Impulse Responses
[Download]
This archive contains three groups of 11 sets of RIRs obtained from a room simulated in CATT-Acoustics modelling software. Each set has a different reverberation time that was varied by changing the absorption coefficient of all six surfaces to produce reverberation times in the interval [0,1] s. The room was shoebox-shaped with dimensions 6×4×3 m (l×w×h). The impulse responses were calculated with the receiver located in the centre of the room at a height of 2 m and the source at a distance of 1.5 m. The omnidirectional sound source was placed at head height on the frontal azimuthal plane (±90°) in 5° increments.
The sets are provided in three groups, with each group corresponding to a different receiver configuration. The three receiver configurations were: binaural, spaced omnidirectional, and mono omnidirectional. In the spaced omnidirectional case, the receivers were spaced by 16 cm (the approximate spacing of the ears in the binaural case). The mono omnidirectional case is provided for completeness.
The RIRs are mono or stereo wave files, simulated at 44.1 kHz, 16 bit, but also included down-sampled to 16 kHz.
Requirements: None.
[Top]
 This Max/MSP patcher is designed for conducting MUSHRA (MUltiple Stimulus with Hidden Reference and Anchor, see ITU-R BS.1534) listening tests. The patcher allows the comparison of a number of stimuli (7 by default, although up to 10 is supported) and facilitates repeats. By default, the patcher can compare seven processes applied to three music tracks, with two repeats, making a total of six pages. However, the software can be easily adapted to accommodate a different number of stimuli and/or music tracks and/or repeats; the included documentation describes the procedure in detail.
Requirements: Max/MSP 6 or higher.
[Top]
This Max/MSP patcher is designed for conducting MUSHRA (MUltiple Stimulus with Hidden Reference and Anchor, see ITU-R BS.1534) listening tests. The patcher allows the comparison of a number of stimuli (7 by default, although up to 10 is supported) and facilitates repeats. By default, the patcher can compare seven processes applied to three music tracks, with two repeats, making a total of six pages. However, the software can be easily adapted to accommodate a different number of stimuli and/or music tracks and/or repeats; the included documentation describes the procedure in detail.
Requirements: Max/MSP 6 or higher.
[Top]
 This Max/MSP patcher implements an ABX listening test. The test is a discrimination task, assessing the listener's ability to hear differences in audio files that contain small impairments. The patcher chooses a reference stimulus and a test stimulus, which are randomly assigned to A and B. Either A or B is then randomly assigned to X. This listener must decide whether X is A or B. The patcher chooses the test stimulus from a pool of several audio files. The presentation of each audio file can be repeated a specified number of times. The presentation of all audio files and repeats is randomised.
Requirements: Max/MSP 6 or higher.
[Top]
This Max/MSP patcher implements an ABX listening test. The test is a discrimination task, assessing the listener's ability to hear differences in audio files that contain small impairments. The patcher chooses a reference stimulus and a test stimulus, which are randomly assigned to A and B. Either A or B is then randomly assigned to X. This listener must decide whether X is A or B. The patcher chooses the test stimulus from a pool of several audio files. The presentation of each audio file can be repeated a specified number of times. The presentation of all audio files and repeats is randomised.
Requirements: Max/MSP 6 or higher.
[Top]
 The separation software developed during Chris Hummersone's PhD is available below. It is based upon Palomäki et al.'s (2004) binaural processor for missing data speech recognition in the presence of noise and small-room reverberation. The software generates "cocktail party" mixtures of signals arising from two spatially-separate sound sources in real rooms and attempts to separate them using interaural cues enhanced by models of the precedence effect. Implemented precedence models include those proposed by Martin (1997), Faller & Merimaa (2004), Lindemann (1986) and Macpherson (1991).
Requirements: MATLAB, Signal Processing Toolbox, compatible C compiler (for Mex functions).
[Top]
The separation software developed during Chris Hummersone's PhD is available below. It is based upon Palomäki et al.'s (2004) binaural processor for missing data speech recognition in the presence of noise and small-room reverberation. The software generates "cocktail party" mixtures of signals arising from two spatially-separate sound sources in real rooms and attempts to separate them using interaural cues enhanced by models of the precedence effect. Implemented precedence models include those proposed by Martin (1997), Faller & Merimaa (2004), Lindemann (1986) and Macpherson (1991).
Requirements: MATLAB, Signal Processing Toolbox, compatible C compiler (for Mex functions).
[Top]
